How COVID-19 has impacted the PR Industry: Ayushi Arora Gulyani – Director Media Corridors
Fujitsu Successfully Develops Easy to Handle, Flexible Nanotube Adhesive Sheet Technology with High Thermal Conductivity
Published on April 17, 2020
KAWASAKI, Japan: – Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced the development of the world’s first adhesive sheet composed of carbon nanotubes with extremely high thermal conductivity of up to 100 W/mK (watt per meter per Kelvin)(1).
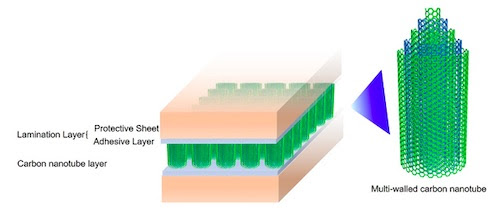
Figure1: Internal structure of carbon nanotube adhesive sheet

Figure 2: Carbon nanotube adhesive sheet
Carbon nanotubes have high thermal conductivity and represent a promising candidate for heat dissipation from heat sources including semiconductor devices. Nevertheless, the material remains difficult to handle due to its fragility, rendering it impractical for many purposes. To address this, Fujitsu has successfully developed a technology for laminating vertically aligned carbon nanotubes, while maintaining their original characteristics of high thermal conductivity and flexibility, as well as a technology for bonding them with sufficient adhesion. This technology facilitates the cutting and handling of carbon nanotube sheets, making it possible to use them as a heat dissipation material, for example, in automotive power modules for electric vehicles (EVs).
Fujitsu aims to license the use of its newly-developed carbon nanotube adhesive sheets to companies in the materials and electrical industries, and will continue to support their use in a variety of commercial applications.
Background and Development
EVs are increasingly being put to practical use as efforts to regulate greenhouse gases accelerate throughout the world. Despite this, the fact that EVs are more expensive than gasoline-powered vehicles and lack similar driving ranges continues to hinder their widespread adoption. In order to improve the cost-performance and driving range in recent years, efforts have been made to develop semiconductor devices that use silicon carbide or gallium nitride as an alternative material to the more commonly-used silicon to reduce the size, weight, power consumption, and cost of power modules for electric vehicles. In order to make this a reality, however, countermeasures to deal with heat generated around semiconductor devices due to module miniaturization must be resolved, and components such as heat dissipation materials and bonding materials that make up modules must be designed to achieve unprecedented levels of heat resistance and thermal conductivity.
Challenges
Carbon nanotubes, a type of nanotechnology material made from carbon atoms, have thermal conductivity that is about 10 times higher than copper. One potential use of this material is its use as a heat sink for dissipating heat from heat sources like semiconductor devices. In 2017, Fujitsu developed a high thermal conductivity sheet using carbon nanotubes, but in order to maintain the sheet shape, the sheet is sintered and molded at an ultra-high temperature of 2000 degrees Celcius or higher, which results in a material that is inflexible. A hard sheet can be attached to flat materials, but it is not suitable for joining materials together that are uneven, which inhibits the places in which the sheet can be applied. Furthermore, in areas around semiconductor devices where reliability is essential, it is necessary to bond both the semiconductor and heatsink via a heat dissipation sheet consisting of carbon nanotubes in order to follow the change in shape caused by temperature differences before and after the device is operated. In general, carbon nanotubes are made adhesive by mixing them into an adhesive material such as resin or rubber, forming a sheet. However, because these adhesive materials have low thermal conductivity, it has been extremely difficult to achieve sufficient levels of both thermal conductivity and adhesion.